
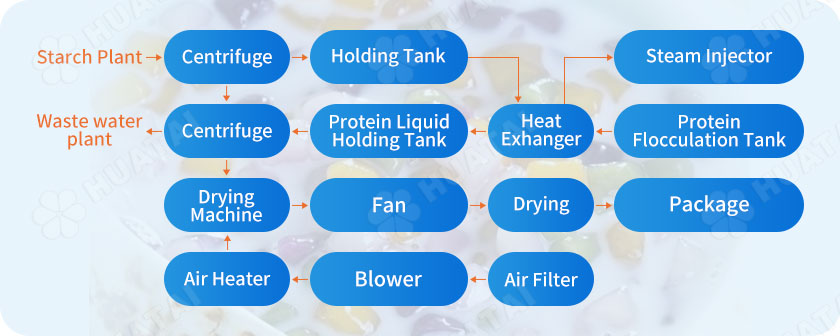
The water separated from potato, sweet potato or cassava cells is cell juice, and the solid content in potato cell juice accounts for about 4-6%. Among them, nitrogen-containing compounds account for 1.6-2.1%, and 50% of nitrogen-containing compounds are proteins.
Protein is the main component of the sap and dry matter of potato starch production cells. The solid content in cell sap contains a large amount of high-grade protein. Typically 65% of the protein in the cell sap water is recovered at this stage. The cell fluid overflowing from the multi-stage cyclone station in the potato starch processing workshop contains soluble and insoluble proteins.
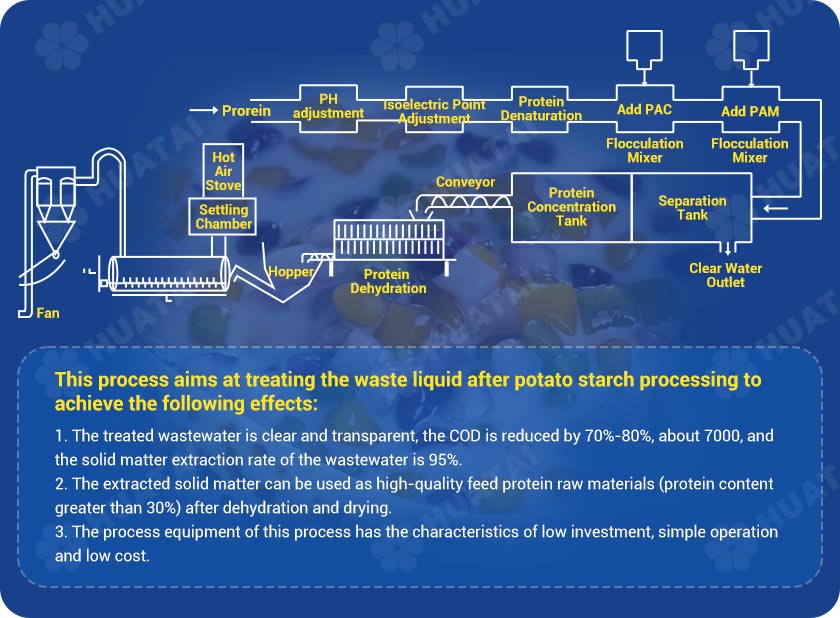
By adjusting the PH value and isoelectric point of the waste liquid, the acidolytic protein is denatured, and the waste liquid is decomposed into colloids. After adding flocculant, the solid matter and water are separated and separated.
After protein extraction from the waste liquid, there are no particulate impurities, the water becomes transparent, and the COD is reduced by 70% to 80%, reaching less than 6000mg/L. The extracted protein material can be used as high-quality feed raw materials after dehydration and drying.
Through continuous research and experiments, we have completed large-scale experiments and practices such as supporting the production of potato starch production lines, obtained relevant data, and developed an application for flocculation extraction of protein from potato wastewater at normal temperature and pressure. Using technology, it has been proven that new methods of extracting protein from wastewater are completely feasible.
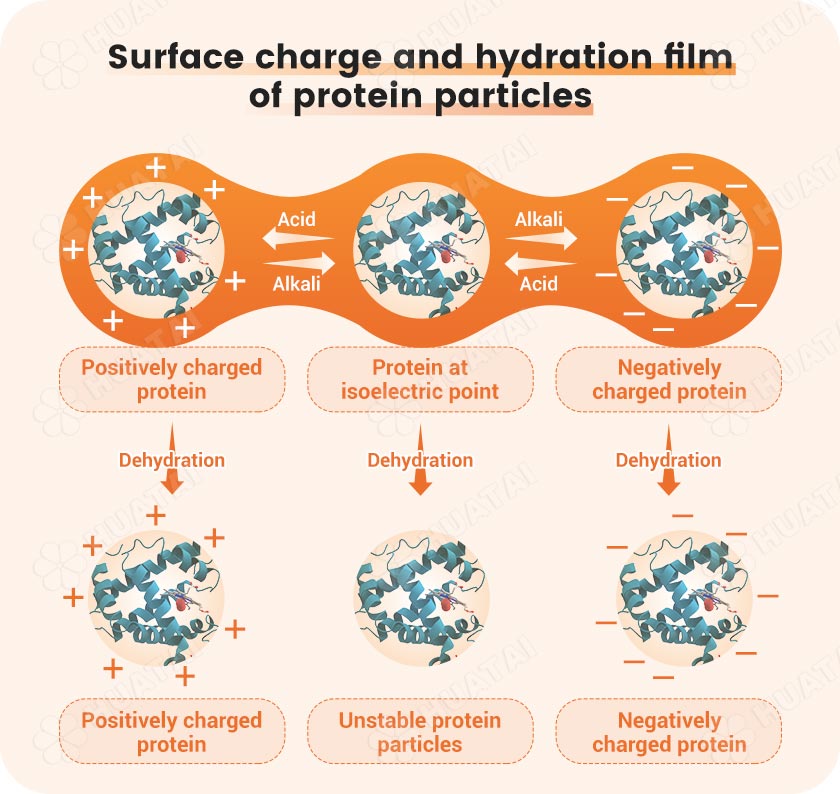
Eggs in water have the same charge and repel each other, and a hydration film can be formed on the surface of the egg, which makes the egg solution (actually a colloid) very stable. For eggs to aggregate with each other, their stability must be destroyed, that is, the hydration film and surface charge must be removed.
Protein is an amphoteric electrolyte, and its isoelectric point is about pH 4.0-5.5. The pH value of starch wastewater is exactly the isoelectric point of the protein.
Therefore, the protein in starch wastewater tends to automatically agglomerate. The flocculation formed by this coagulation method The particles are very small. At the same time, due to the influence of the same charge and hydration layer on the surface of the flocs, the flocs are very unstable.
Adding inorganic polymer flocculant neutralizes the charge on the flocs, making it easier for the flocs to get closer and agglomerate into larger flocs. Adding organic polymer flocculants can make the flocs form more stable ones through adsorption and bridging large flocks.
Inorganic coagulants mainly rely on the charge of neutralized particles to agglomerate into flocs, while organic flocculants mainly rely on adsorption and bridging to agglomerate the flocs into flocs. Inorganic coagulants are added first to neutralize the charges, and then Organic flocculants generate flocs. Since the specific gravity of flocs is smaller than water, protein, and water can be separated.
In the potato protein solution, the tendency and degree of amino acid dissociation into cations and anions are equal. The net charge is zero and it is electrically neutral. The pH of the solution at this time is called the isoelectric point of the amino acid.
The charge carried by amphoteric ions changes due to the pH value of the solution. When the positive and negative charges of the amphoteric ions are equal, the pH value of the solution is its isoelectric point.
When the pH of the external solution is greater than the pH of the zwitterion, the zwitterion releases protons that are negatively charged. When the pH of the external solution is less than the pH of the zwitterion, the zwitterion becomes protonated and becomes positively charged. The solubility of amino acids in solution is minimal when the isoelectric point is reached.
Proteins in aqueous solutions carry the same charge and repel each other, and the protein surface can form a hydration film, which makes the protein solution (actually a colloid) very stable.
The application of this technology is different from food-grade protein extraction. In comparison, it has the advantages of low investment cost, low operating cost, and low maintenance cost. It can realize PLC control of the entire protein extraction process and can also realize environmental protection data in the production process. detection and sharing.
The recovered protein will not change in amino acid structure and has extremely high nutritional value. It is a good feed additive.
The COD in the wastewater will be reduced to less than 6000mg/L, and the SS will be reduced by 95%. This not only reduces environmental pollution but also extracts valuable proteins from the wastewater, truly realizing the purpose of energy conservation and environmental protection.
China’s current import of soybean meal from abroad has been greatly reduced, and the demand for protein feed in the feed industry will further increase. Potato protein will be the best choice to replace soybean meal in the feed industry, so the price of potato protein will also increase in the future. Continuously rising, bringing higher profits to the company.
After extracting protein from potato starch production wastewater, the odor is eliminated and the amount of land used for irrigation is reduced. It is also the focus of the potato, sweet potato and cassava industry chain. This application technology benefits the country and the people. It has contributed to the contemporary era and will have an impact on the development of society. Bring powerful impetus.