
Since production wastewater contains protein, it is easy to produce a large amount of foam. If the wastewater is not treated in time, the protein-containing wastewater will stink, and direct discharge may cause environmental pollution.
The cell fluid overflowing from the multi-stage cyclone station in the potato starch processing workshop contains soluble protein and insoluble protein. For soluble protein, we use special flocculation extraction technology to extract the protein from the aqueous solution.
First, based on the principle that protein has the lowest solubility at the isoelectric point, a part of the protein can be precipitated. Therefore, a certain amount of hydrochloric acid is added to the potato cell fluid to adjust the pH value of the solution to the isoelectric point of the protein. At the isoelectric point, part of the protein will precipitate out, which is the extraction of industrial feed protein.
However, since different proteins have different isoelectric points, precipitation cannot rely solely on the isoelectric point. After precipitating part of the protein, we use the protein thermal coagulation method to continue extracting the protein in the solution to maximize protein extraction.
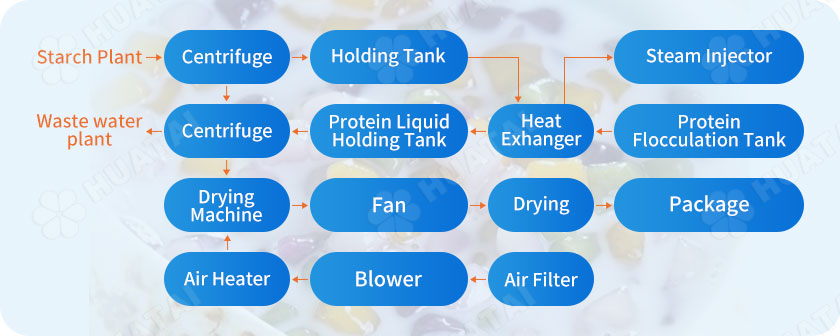
During the production process, the cell fluid in the starch workshop enters the decanter centrifuge through the pipeline to separate small particles such as fiber and starch.
The separated cell fluid is transported to the buffer tank by a pump to ensure the stability of the production line feed and the entire protein extraction system.
A defoaming device is installed on the buffer tank to ensure that the workshop is clean and tidy. An acid-adding port is installed to adjust the pH value of the cell serum.
The cell liquid is transported to the tube-type heat exchanger by the feed pump. In the heat exchanger, it conducts heat exchange with the thermally flocculated protein liquid for preheating. The cell liquid temperature is preheated to above 60°C. After heat exchange, After the shell process, it enters the high-efficiency steam ejector at high speed.
The steam enters the high-efficiency steam ejector at high speed through the steam pipe, and exchanges heat with the cell serum in the mixing chamber. In the mixing tube, vigorous energy exchange continues to occur, which increases the temperature of the cell solution. In this process, the protein liquid The protein inside is flocculated, and finally mixed evenly and flows out of the high-efficiency steam ejector and into the protein flocculation tank.
The protein flocculation tank maintains a higher temperature, and the protein liquid continues to flocculate during this process to achieve a higher extraction rate.
The flocculated protein liquid enters the tube side of the tube-and-tube heat exchanger under the action of gravity. The temperature of the protein liquid drops to about 60°C and then enters the protein liquid buffer tank.
The protein liquid is transported to the decanter centrifuge by the screw pump, the light-phase liquid is transported to the sewage treatment plant through the sewage pipe network, and the heavy-phase protein is transported to the flash dryer for drying by the auger.
The cold air is heated by the heat exchanger and then enters the stirring, crushing, and drying chamber. The larger and wetter material particles at the bottom of the dryer are mechanically crushed under the action of stirring, and the particles with lower moisture content and smaller particle size are crushed by the rotating airflow. The entrainment rises and enters the airflow drying system from the top airflow outlet for secondary drying and separation.
The protein material dried by the flash dryer is transported by the fan to the drying tube for secondary drying. The purpose of adding a drying system is to increase production capacity and ensure the moisture stability of the finished protein. After drying, the protein is processed through a cyclone separator protein and The exhaust gas is separated, and the finished protein is packaged by a packaging machine and put into storage.